No, a car battery won't recharge itself if it's completely dead without a jump-start. However, if your battery has some charge left, it can regain power while the car runs. The alternator converts the engine's mechanical energy into electrical energy, recharging the battery in the process. Keep in mind that driving effectively can speed up this recharging. Idling alone isn't as efficient. To ensure your battery remains healthy, regular maintenance and monitoring are key. Curious about how to keep your battery in top shape? There's more to explore about battery care and performance.
Key Takeaways
- A completely dead car battery cannot recharge itself without an external power source like a jump start.
- A partially charged battery can self-recharge when the car is running, utilizing energy from the alternator.
- Idling is less effective for recharging; driving the car improves alternator output and battery charging.
- Heavy electrical loads can hinder the self-recharging process, making regular maintenance essential for battery health.
- If the battery is low, proactive monitoring and maintenance can help prevent breakdowns and extend its lifespan.
Can a Battery Recharge Itself?

When it comes to car batteries, the question of whether they can recharge themselves is straightforward. A dead car battery can't recharge itself. If your battery's completely drained, you'll need to jump-start it or connect it to a charger to regain power. Without an external power source, your battery will remain lifeless.
However, if your battery still has some charge, it can recharge itself while the car's running. The alternator supplies excess energy, but driving without heavy electrical loads is key to recharging efficiently. If you're using power-hungry features, you'll hinder the process. Additionally, regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring your battery remains in good condition to support its ability to recharge effectively.
To revive a dead battery, jump-starting from another car is common. Alternatively, you can use a battery charger, which takes time but can fully recharge it. Driving can also help, but only if the battery isn't completely dead. If you find yourself frequently needing to recharge, replacing the battery might be your best option.
Be aware of limitations, though. A completely dead battery mightn't recover. Also, improper charging can lead to damage, so regular maintenance is essential for keeping your battery in good shape.
Understanding the Alternator's Role
The alternator plays a vital role in your vehicle's electrical system by converting mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy. It uses the engine's belts to turn a rotor inside the alternator, generating alternating current (AC). This AC is then converted to direct current (DC) to recharge your battery.
While the engine runs, the alternator powers essential electrical components like lights, the radio, and GPS.
Key components of the alternator include the rotor, which spins fast with magnets; the stator, a set of conductive copper wiring; and the voltage regulator, which controls energy flow to prevent overcharging. The voltage regulator is essential for maintaining optimal voltage levels to ensure the vehicle's electrical systems function properly.
The belts driven by the engine keep everything moving, while electrical connections transmit power to the battery and other systems.
As the alternator recharges the battery, it ensures you have enough power to start the engine repeatedly, preventing premature battery failure. It operates in a circuit with the battery, providing continuous power.
Keep in mind that a healthy battery is crucial for optimal alternator performance. Regular checks can help maintain your vehicle's electrical system and overall reliability.
Jump-starting a Dead Battery
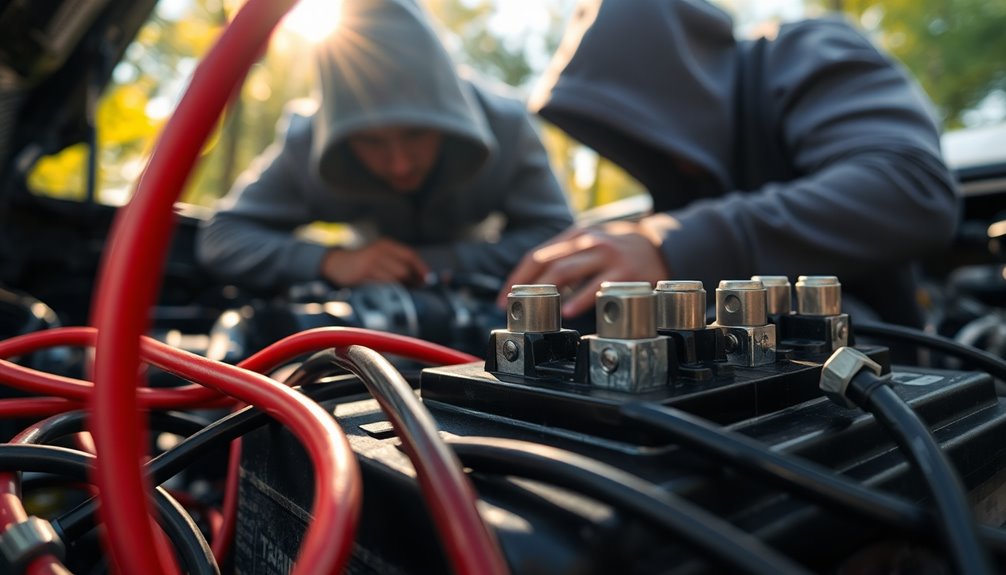
If you find yourself with a dead battery, knowing how to jump-start it can save you from being stranded.
First, park the working car close enough to the dead car without touching. Turn off the engines, engage the parking brakes, and ensure both cars are in park or neutral. Pop the hoods and check the batteries for any leaks or corrosion.
Next, grab your jumper cables. Connect the red clamp to the positive terminal of the dead battery, then to the positive terminal of the working battery. Attach the black clamp to the negative terminal of the working battery and the other black clamp to an unpainted metal surface on the dead car. Avoid letting the cable ends touch. Make sure your jumper cables are in good condition before starting the process to prevent any issues.
Start the working car and let it run for a few minutes. Then, try starting the dead car; it might take a few attempts. If it doesn't start immediately, give it a moment and try again.
Once it starts, let it run for several minutes. Finally, remove the cables in the reverse order, and drive the revived car for at least 15-20 minutes to help recharge the battery fully.
Alternative Methods for Recharging

While traditional methods like jump-starting can be effective, there are several alternative methods for recharging a car battery that may suit your situation better.
One of the simplest ways is using the alternator. Just make sure your engine is running, then let it idle for at least 30 minutes, or drive for about 30 minutes to an hour at a steady speed. Higher RPMs can also help recharge a flat battery faster, especially when using the alternator to maintain battery health.
If you have a manual transmission, you can try push starting the car. Grab a friend, find a clear area, and shift into a low gear with the clutch pressed. As they push, slowly release the clutch to start the engine.
Another option is a portable jump starter. Ensure it's fully charged, connect the cables correctly, and let it charge the battery for a few minutes before starting the engine.
Lastly, consider solar or external power charging using a solar panel or a portable power station. Just check compatibility and monitor the temperature to avoid damaging the battery during slow charging.
Each of these methods can get you back on the road in no time!
Recognizing Signs of a Dead Battery

After exploring alternative methods for recharging your car battery, it's important to recognize when a battery is on the verge of failure. One of the first signs you might notice is slow starting; if your engine takes longer to crank or you hear a clicking sound when turning the key, it's a red flag. Dim headlights and non-functioning electrical components, like the radio, also indicate insufficient power. Additionally, a battery test can help determine if the battery is indeed failing.
Pay attention to any odd smells, especially a rotten egg scent, which suggests gas venting from the battery. A swollen battery case or visible damage can signal internal issues. If your battery's age exceeds four to six years, it's time to inspect it closely.
Other indicators include difficulty starting the car even when lights and accessories work. If you hear grinding sounds or experience increased effort with brakes or steering, your battery might be failing.
Finally, a complete failure, where the battery won't take a charge and requires external assistance, is the last sign you need to watch for. Recognizing these symptoms early can save you from being stranded.
Impact of Driving on Recharge

Driving your car not only gets you from point A to point B but also plays a crucial role in recharging your battery. When you drive, the alternator converts mechanical energy from your engine into electrical energy, powering your vehicle's systems and replenishing the battery. The higher your engine RPMs, the more efficiently the alternator works, enhancing the charging process.
If you drive at highway speeds—around 55 MPH or higher—you'll maximize your battery's recharge. Longer drives allow the alternator to operate at higher RPMs for an extended time, which is especially beneficial for heavily discharged batteries. In fact, a full recharge may take anywhere from 30 minutes to several hours of continuous driving, depending on battery condition.
On the flip side, frequent stops and idling reduce charging efficiency due to lower RPMs, making driving a much more effective option.
While idling can maintain or slightly boost your battery's charge, it simply can't compete with the efficiency of driving. Idling results in lower alternator output, meaning it could take hours to recharge a dead battery compared to the faster results of a good drive.
Safety Considerations for Jump-starting

Jump-starting a car battery can be a straightforward process, but it's essential to prioritize safety to avoid accidents or injuries. Start by ensuring both vehicles are turned off, parked, and have their parking brakes engaged. Keep keys away from the ignition to prevent accidental starts.
Check the battery for low electrolyte levels or freezing, as you should never jump-start a compromised battery. During the process, avoid letting cable ends or vehicles touch to prevent electrocution. Remove any jewelry to reduce the risk of electrical shock and wear eye protection to safeguard against potential battery explosions. Removing jewelry minimizes the chance of electrical accidents, especially around battery terminals.
Clear the area around both vehicles for safety. When connecting cables, attach the positive cable to the dead battery first, followed by the good battery. For the negative cable, connect it to the good battery and then to a bare-metal surface in the dead vehicle's engine bay, avoiding the dead battery's terminal to prevent sparks.
Ensure cables are suitable for the current required and avoid stretching them. After jump-starting, let the booster vehicle run for a few minutes before attempting to start the dead vehicle. Always follow proper procedures to ensure safety throughout the process.
Best Practices for Battery Maintenance

Maintaining your car battery is crucial for ensuring reliable performance and longevity. Start by regularly cleaning the battery surface with a damp cloth or a battery cleaning solution to prevent short circuits. Make sure the terminals are free from dirt and buildup, and use terminal spray to ward off future corrosion. If you notice any corrosion, clean it off promptly.
When it comes to charging, remember that your battery recharges while driving, thanks to the alternator. Avoid running headlights or electronic devices with the engine off, as this can shorten your battery's lifespan. If your car sits idle for long periods, consider using a trickle charger to maintain the charge. Routine maintenance practices can significantly enhance your battery's performance and longevity.
Your driving habits also play a vital role. Try to limit short trips, as they can drain the battery quicker than longer drives, which allow for full recharging. Before turning off the engine, ensure all electrical components are off to avoid unnecessary battery drain.
Finally, store your battery in a cool, dry place and check water levels regularly if it's not maintenance-free. By following these best practices, you'll keep your battery in top shape and extend its life.
When to Replace Your Battery

Knowing when to replace your car battery is essential for avoiding unexpected breakdowns. Typically, car batteries last between 3 to 5 years, but factors like driving frequency and temperature can affect their lifespan. Regular checks are particularly important for older batteries to ensure they are still functioning effectively.
If you notice your car struggling to start, it could be a sign your battery is failing. Frequent jump-starts or slow engine cranking are red flags you shouldn't ignore.
Keep an eye out for physical signs as well. A bulging battery case, unpleasant sulfuric smells, or corrosion on the terminals can indicate serious issues. These signs not only affect efficiency but could also pose safety hazards.
Don't overlook electrical problems either. Dim headlights, slow power windows, or malfunctioning accessories may point to a dying battery. If your check engine light comes on, it might be due to low battery voltage as detected by your car's sensors.
To check your battery's health, measure the voltage; a healthy battery should read at least 12.6 volts. If it's significantly lower, it may be time for a replacement.
Staying proactive can save you from inconvenient and costly breakdowns.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a Car Battery Be Completely Dead and Still Hold a Charge?
A completely dead car battery can't hold a charge. When it's dead, it lacks the necessary voltage to power anything, including starting the car.
Even if you try charging it, a dead battery often won't respond without external help. Regular maintenance and checks can prevent it from dying completely.
If you notice issues, it's best to address them before the battery reaches that point. Otherwise, you'll face a frustrating situation.
How Long Does It Take for a Car Battery to Recharge While Driving?
When driving, it usually takes between 30 minutes to several hours for your car battery to recharge, depending on several factors.
If your battery's moderately discharged, you might notice a quicker recharge. Highway driving at speeds over 55 MPH is more efficient than stop-and-go traffic.
Also, if you minimize electrical loads while driving, you'll help your battery recharge faster.
What Factors Affect How Quickly a Battery Recharges?
Several factors affect how quickly your battery recharges. The battery's capacity and type play a significant role, with larger batteries taking longer.
The charging rate of the station, whether AC or DC, also impacts speed. Additionally, the state of charge matters; batteries charge faster when nearly empty.
Environmental conditions, like temperature, can slow down the process, too. Older or damaged batteries may struggle to accept charges efficiently, affecting overall recharge time.
Can Extreme Temperatures Damage a Car Battery's Ability to Recharge?
Extreme temperatures can definitely damage your car battery's ability to recharge.
When it gets too hot, the electrolyte can evaporate, leading to corrosion and quicker discharges. High heat also strains the alternator, making it harder to recharge the battery.
If you're parked in the sun, try to find shade or a garage to protect your battery. Regular maintenance and inspections can also help prevent heat-related issues, ensuring better performance.
Is It Safe to Recharge a Battery That Has Been Leaking?
It's not safe to recharge a leaking battery. If you notice any signs of leakage, like acid spills or corrosion, you should avoid charging it.
First, disconnect the battery and assess its condition. If it's damaged or swollen, replace it instead of trying to recharge.
Always wear protective gear and work in a well-ventilated area. Safety's your priority, so handle leaking batteries with care and consider professional help if needed.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a car battery can't recharge itself without some help. While the alternator works to replenish the battery while you drive, a completely dead battery often needs a jump-start or alternative methods to get back in action. Keeping an eye on your battery's condition and practicing routine maintenance can help extend its life. If you notice signs of failure, don't hesitate to replace it to avoid being stranded. Stay proactive and keep your vehicle running smoothly!










